Head and Neck Cancer Treatment in Iran Details
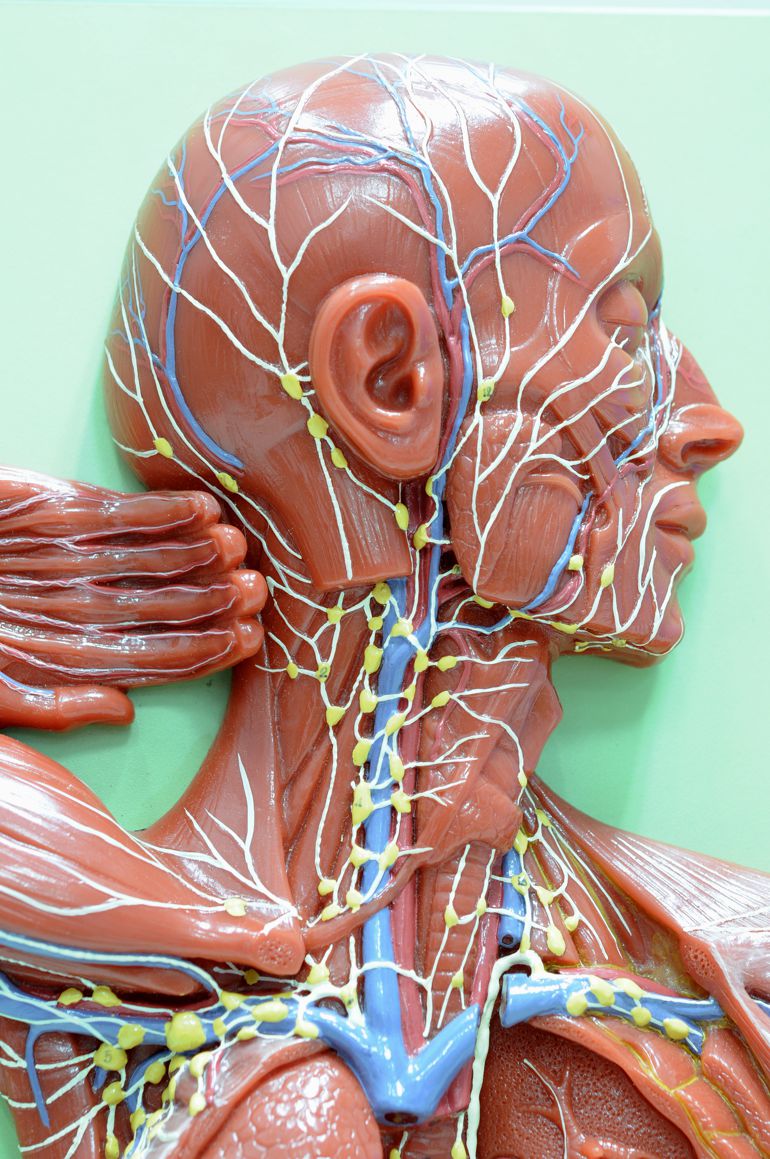
What are the Head and Neck Cancers?
Head and neck cancers generally start in the squamous cells lining the moist mucosal surfaces within the head and neck.
The squamous cells are known as squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck.
These cancers may also start in the salivary glands although salivary gland cancers are not so common.
There are several salivary gland cancers as these glands have different types of cells that may become cancerous.
Types of Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancer can be categorized into five main types that are named after the body part from where they start.
Five main types include the followings:
Nasopharyngeal Cancer
The nasopharynx is the airway passageway at the upper part of the nose at the back of the nose.
Salivary Gland Cancer
Saliva produced by the salivary gland is the fluid that is released within the mouth to keep the mouth moist.
Mouth helps in breaking down the food as it contains certain enzymes.
Hypopharyngeal and Laryngeal Cancer
A tube-shaped organ located in the neck used for swallowing, breathing, and talking is the larynx.
The hypopharynx also referred to as gullet, is the lower part of the throat surrounding the larynx.
Oropharyngeal and Oral Cancer
Both tongue and the mouth are included in the oral cavity.
The middle part of the throat is included in the oropharynx.
Paranasal Sinus and Nasal Cavity Cancer
The air-filled areas surrounding the nasal cavity is known as the paranasal sinuses.
The space at the back of the nose from where air passes on the way to the throat is known as the nasal cavity.
Symptoms of Head and Neck Cancer
- A sore on the skin which fails to heal or is ulcerated, changes in a mole or discoloration
- A sore in the mouth that is not healing
- Persistent sore throat
- Dentures that are no longer fit
- Numbness in other areas and the tongue
- Swelling or a lump in the neck
- White or red patch in the mouth
- Difficulty in swallowing, chewing and in moving tongue and jaws
- Blood in the sputum
- L, the opening of teeth
- Persistent change or hoarseness in the voice
- Frequent, ongoing nasal congestion, nosebleeds or chronic sinus, infections that do not respond to any treatment
- Pain in ears, throat, and neck
Diagnosis of Head and Neck Cancer
Urine and blood test /Physical examination
Lumps in the cheeks, lips, neck, and gums are examined by performing a physical examination of a patient.
Abnormalities are also noticed by inspecting throat, nose, tongue, and mouth.
Cancer can be diagnosed by performing urine and blood tests.
Biopsy
A small amount of tissue is removed for examining under a microscope for diagnosing head and neck cancer.
X-ray
This helps in creating pictures of the structures within the body by using little radiation.
A barium swallow can identify the abnormalities of the swallowing passage.
Endoscopy
The inside of the body can be viewed by using a flexible and light tube known as an endoscope.
The head and neck areas are examined by inserting this tube through the nose into the throat.
Ultrasound
The picture of the internal organs is created by performing an ultrasound that uses sound waves.
Bone Scan
Radioactive tracer is used for looking inside the bones.
This tracer is injected into the vein of a patient.
This is detected by a special camera as it gets collected in the bone areas.
The gray color appears representing a healthy bone, and dark color represents the injured areas due to cancer.
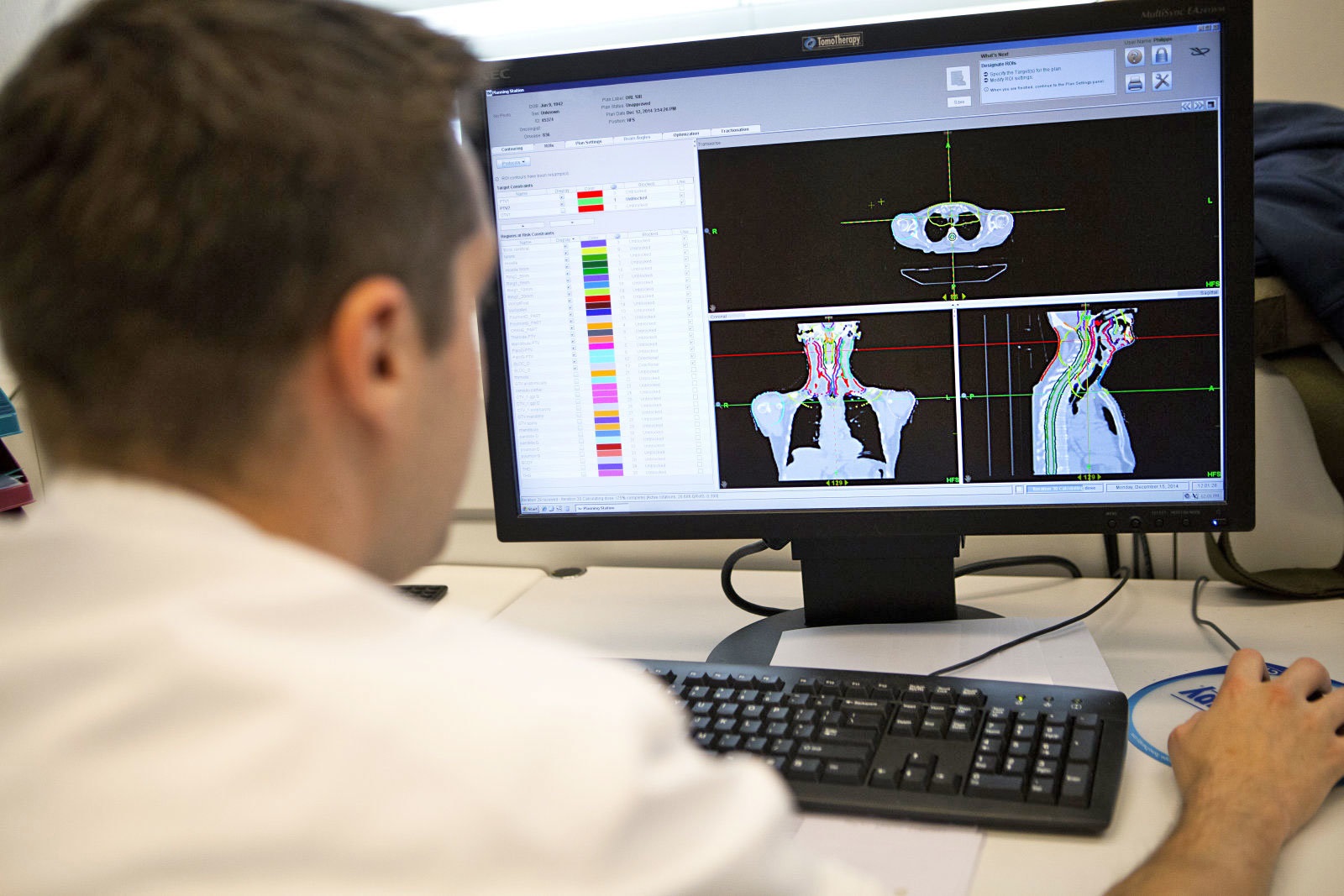
Computed Tomography Scan
A tumor or abnormalities of the head and neck are viewed by performing computed tomography (CAT or CT) scan.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan
By means of this scan, the pictures of tissues and organs within the body are created.
The injection of a radioactive substance is done into the body of a patient.
The tissues and organs that use most of the energy absorb this radioactive substance.
Cancer tends to use power actively, thereby absorbing more radioactive substance.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
The detailed images of the body that include the base of the tongue and the tonsils are produced by performing an MRI that makes use of magnetic fields.
Panorex
The x-ray of lower and upper jawbones is performed for detecting cancer or for evaluating teeth before chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Head and Neck Cancer Treatment
Chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy are the three main types of treatment for administering head and neck cancer.
Surgery or radiation therapy is considered as the primary treatments, while chemotherapy is usually used as an adjuvant or additional treatment.
Primary cancer can be easily treated with the help of radiation therapy.
Radiation therapy can also effectively treat the neck.
A neck dissection is also sometimes necessary for removing involved lymph nodes in the neck when the amount of disease in the neck nodes is very wide.
Surgery is considered as an essential treatment that can be done either before or after radiation therapy.
Radiation therapy is given afterward when it is necessary to remove the primary tumor surgically.
The tumor is first tried to shrink by using radiotherapy, and surgery is followed by radiotherapy.
Following radiation, therapy procedures are used for treating head and neck cancer:
- Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): The specific areas inside the tumor or malignant tumors are targeted by this high-precision radiotherapy that makes use of computer-controlled x-ray accelerators that delivers precise radiation doses.
The high-intensity radiation beam is focused on the tumor to damage it without disturbing any surrounding healthy cells. - External Beam Therapy (EBT): Through this therapy, high-energy beam x-rays are delivered at the location of the tumor.
The tumor site is the target of this beam, and it can destroy cancer cells while sparing nearby healthy tissues.
There is no placement of radioactive sources in the body of a patient.