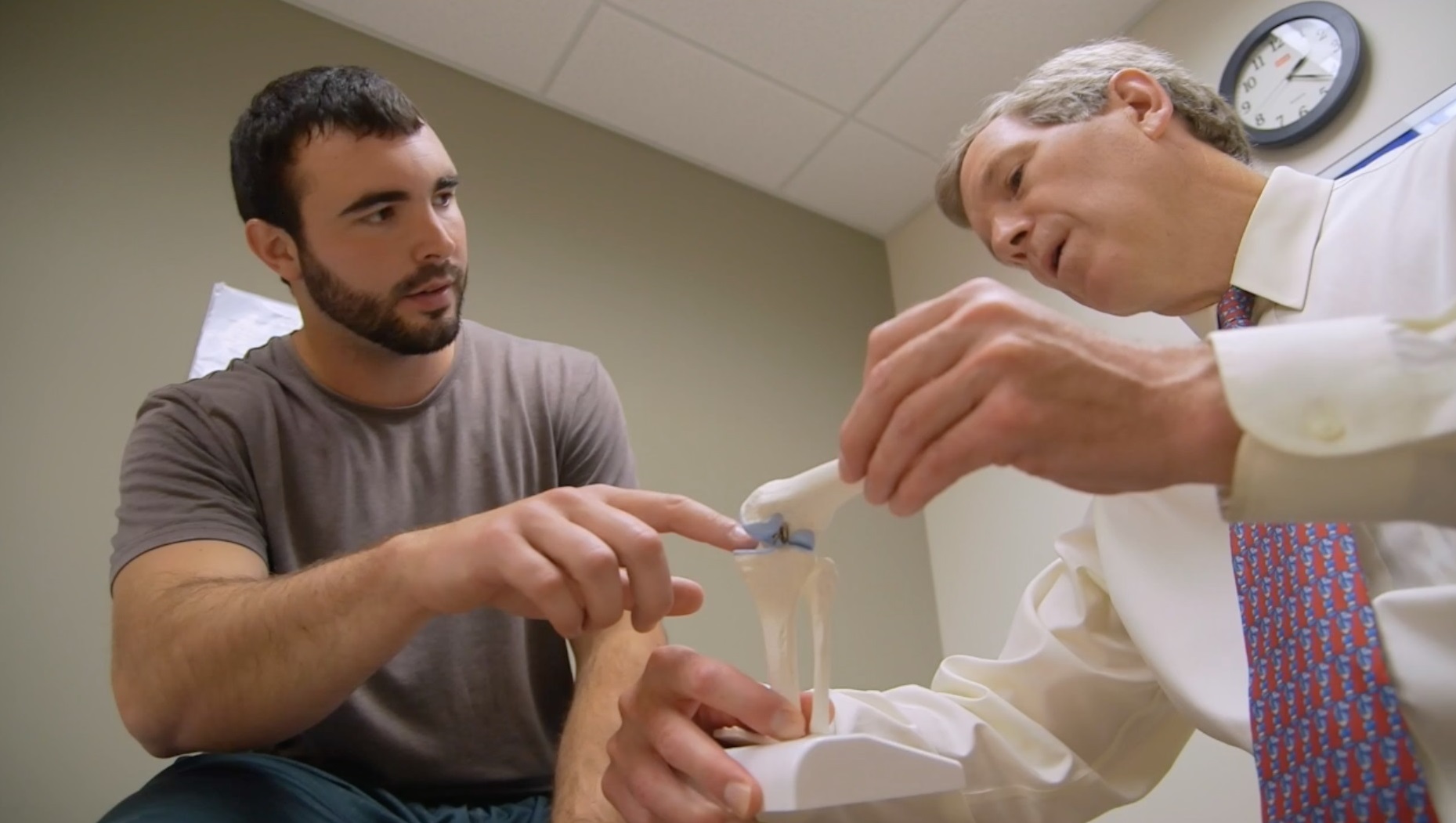
Orthopaedic Surgical Oncology in Iran Details
What is Orthopedic Oncology?
Orthopedic Oncology is the procedure by which both malignant and benign tumors occurring in different parts of the body are first diagnosed and then treated.
Orthopedic Oncology Diagnosis and Treatment
Benign Bone Tumor
Benign Bone Tumors (non- cancerous) does not spread to the other parts of the body.
These tumors may destroy the bone, and surgical treatment is required to remove the tumor and thereby to restore the bone health.
Types of bone tumors:
- Benign Lesions
- Unicameral Bone Cyst
- Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
- Osteoblastoma
- Enchondroma
- Unicameral Bone Cyst
- Giant Cell Tumor
- Osteoid Osteoma
- Fibrous Dysplasia
- Chondromyxoid Fibroma
- Osteochondroma
Malignant Bone Tumor
These cancerous tumors require early treatment at the start of the disease.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are the treatments required either before or after the surgery.
The surgery aims to remove the entire diseased bone to avoid amputation and thereby to restore the appearance and function of the diseased area. Its types are:
- Malignant tumors of bone
- Osteosarcoma
- Metastatic Carcinoma
- Chondrosarcoma
- Ewing’s Sarcoma
- Metastatic Carcinoma
- Multiple Myeloma
Lesions of Joints
They generally occur in the form of capsules of joints like shoulder, foot, hip, knee, elbow, or wrist.
These lesions can develop and harm or create pain in the joint.
The surgical procedure is done to remove the lesion of the joint and thereby restoring the health and function of the diseased area.
Its types are:
- Tenosynovial Giant Cell Lesion
- Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis
- Synovial Chondromatosis
Soft Tissue Sarcomas
These tumors mostly arise either in fat or muscle and not in the bone.
They can be both malignant and benign.
These tumors are rare and generally develops in the pelvic area or the limbs.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are the two treatments available that are done either before or after the surgery.
The types are:
- Malignant soft tissue lesions
- Liposarcoma
- Malignant fibrous histiocytoma
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Fibrosarcoma
- Synovial cell sarcoma
Bone Cancer Treatment
It is a serious condition where there is a growth of abnormal cells in the bone that could be benign or cancerous.
The abnormal growth usually occurs in the areas of fast growth, and the reason for this bone tumor is still unknown.
Probable causes could be trauma and radiation or inherited mutations.
In most cases, no reason is found for this cancerous condition.
Types of Bone Tumor
- Giant Cell Tumor: This tumor is made up of a great number of non-cancerous cells that forms an aggressive tumor.
The tumor generally occurs near the end of the bone and close to a joint.
The knee is the location of a tumor, but it can also include flat bones like breastbone (sternum) or pelvis, or the bones of the legs and arms.
The giant cell tumor is usually covered by new bony growth. - Chondroblastoma: This tumor is of the rare type and affects people of every age.
It is generally found in the epiphyses of long bones before the closure of epiphyseal.
The Chondroblastoma accounts for five percent of benign bone tumors and is found in the centers of ossification.
The tumors are probably found in the humerus, further in the femur and lastly in the tibia.
The tumor of Chondroblastoma can be found in union with the aneurismal bone cysts. - Enchondroma: This tumor initiates from the cartilage and is of the type of non-cancerous bone tumor.
Cartilage is found in the adults and is a type of stringy connective tissue from where most bones build up.
Enchondroma tumor largely affects the cartilage that outlines in the bones. - Osteochondroma: Osteochondroma (osteocartilaginous exostoses) is a tumor where there is an overgrowth of bone and cartilage close to the end of the bone near the growth plate. Osteochondroma mostly affects the long bones in the scapula, leg, or the pelvis.
Bone Grafts
It transplants the bone tissue, and the bone grafts are used to rebuild and repair the diseased bones in knees, spine, hips, and at times in other joints and bones.
The bone loss that has been caused by cancers or fractures can also be repaired with bone grafts.
When the body grafts are accepted by the body, then it helps in providing the growth of new living bone.
When the bone graft (transplanted) comes from the other person, then it is termed as an allograft.
While in autograft, the bone comes from either from leg, hips or ribs.
Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is a new and minimally evasive procedure used for treating cancer.
This surgery is more precise as compared with standard laparoscopy and open surgeries.
By using this surgery, the patients can get more accurate and precise results of the troubled region which also result in decreased blood loss.
Robotic surgery uses customized treatments which are held by a robotic arm, and the procedure needs small incisions that can lessen the trauma to the tissues.
The procedure is very safe and involves less pain and complications.
The recovery period is also faster and requires a short stay at the hospital.