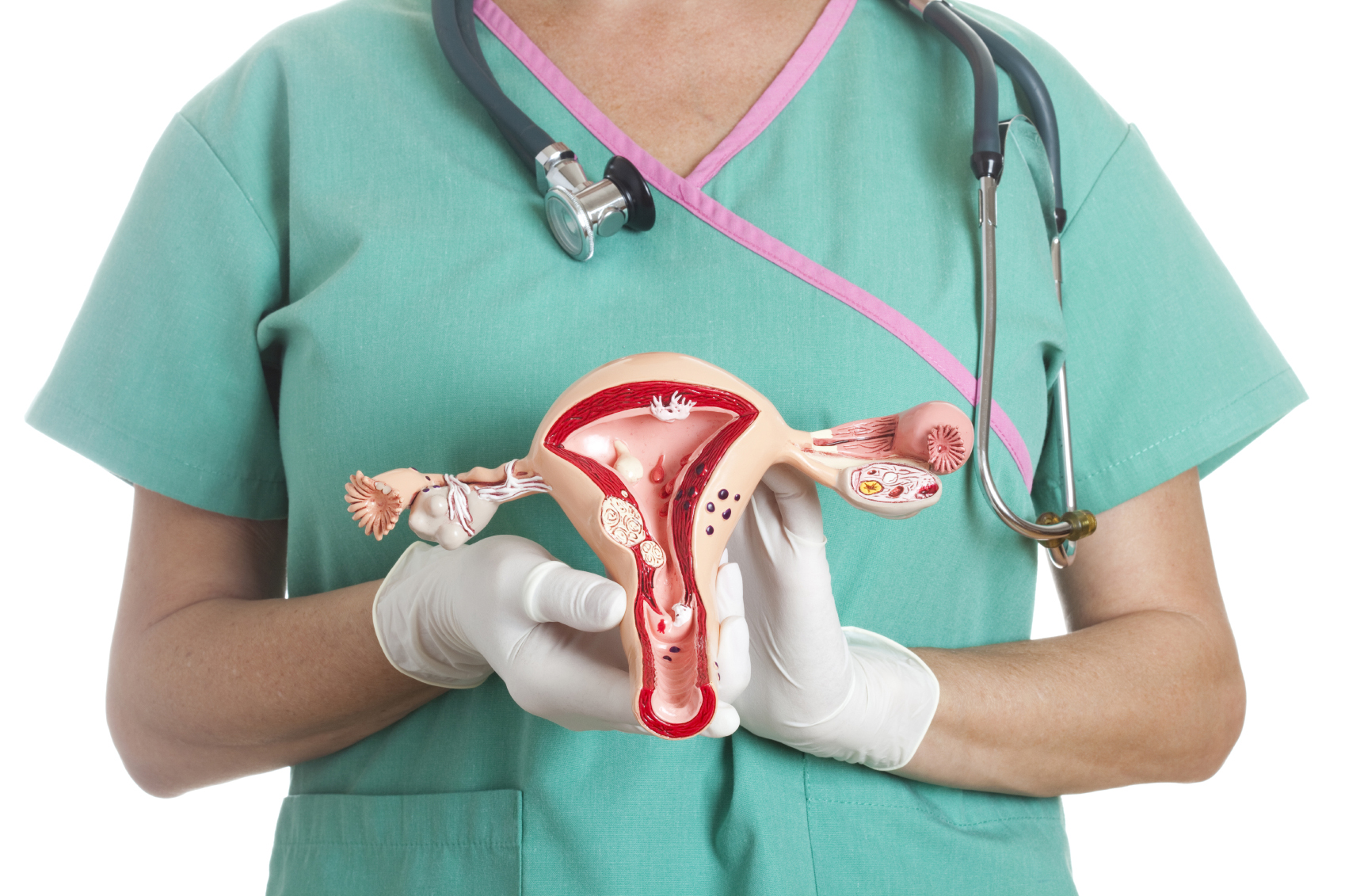
Ovarian Cancer Treatment in Iran Details
What is Ovarian Cancer?
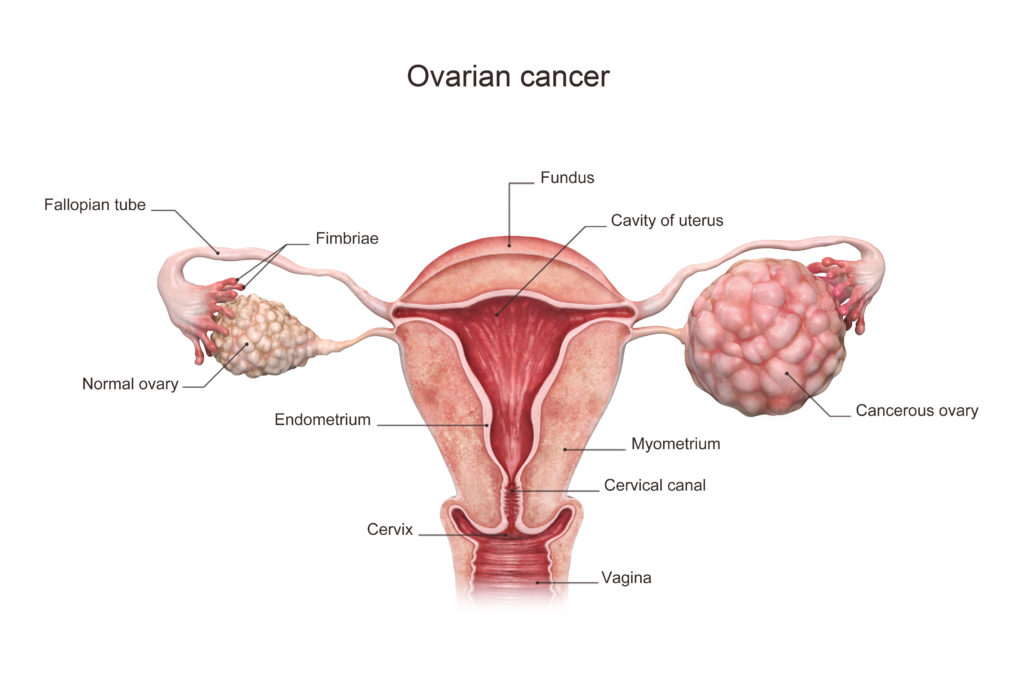
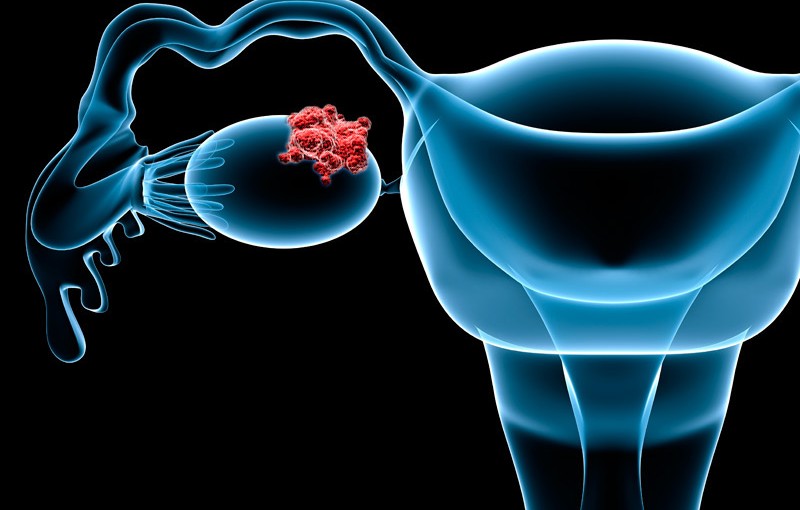
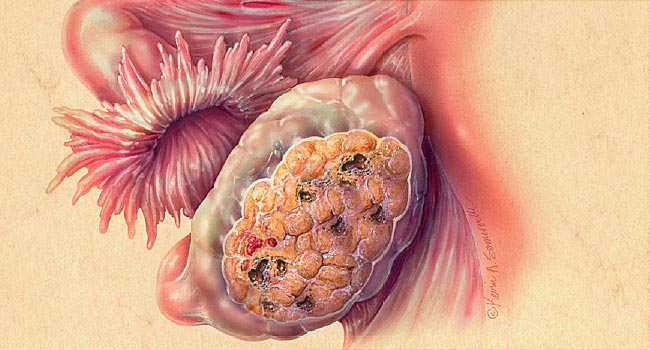
A cancerous growth that develops in many different parts of the ovary is known as ovarian cancer.
Ovaries are a pair of female reproductive glands that helps in the formation of eggs or ova.
Several ovarian cancers occur from the epithelium (outer lining) of the ovary.
Most of these cancers are either malignant germ cell tumors or ovarian epithelial carcinomas.
Types of Ovarian Tumors
Several tumors may start in the ovaries.
These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
These tumors can be categorized into the following types:
Stromal Tumors
These tumors begin from those cells that are responsible for holding the ovary together and for making female hormones.
Germ Cell Tumors
These tumors begin from those cells that are responsible for producing the eggs.
Epithelial Tumors
These tumors begin from those cells which cover the outer surface of the ovary.
Most ovarian tumors are epithelial tumors. Serous is considered as the most common type of epithelial cancers.
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is considered as one of the most common cancer among women.
Some of its major causes include the followings:
- The usage of hormone replacement therapy for more than five years especially when the only estrogen is used
- Inherited gene mutation
- Women who are 50 years or above
- Obesity
- Family history of breast cancer or ovarian cancer
- Having never been pregnant
- Having had cancer before such as colon, breast or uterine
Early Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
- Changes in bowel habits like constipation
- Pelvic pain
- Heartburn or indigestion
- Pain on the lower side of the body
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Back pain
- Urgent and more frequent urination
- Pain in the lower stomach
- Feeling full rapidly while eating
The progression of ovarian cancer may result in following symptoms that include the followings:
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Breathlessness
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
Stages of Ovarian Cancer
Stage 1
In the very first stage, cancer growth is limited to the ovaries or ovary.
Stage 1A
Here, the cancer growth is only in one ovary, and the tumor is there within the ovary.
No cancer can be seen on the outer surface of the ovary.
Also, no Ascites are present that contain malignant cells.
Here the capsule is also intact.
Stage 1B
The cancer growth is restricted to only ovaries, and there is no tumor present on the outer surfaces of these ovaries.
Also, no Ascites is present that contain malignant cells.
Here also the capsule is intact.
Stage 1C
The tumor can be stage 1A or stage 1B, and some of the conditions may also be present – Ascites are there that contain malignant cells, the tumor is present on the outer surface of one or more ovaries, or the capsules has broken.
Stage 2
The second stage is categorized with the cancer growth that includes one or both ovaries with pelvic extension.
Stage 2A
Cancer may have extended to, or it may also involve Fallopian tubes or the uterus. Sometimes both can also be involved.
Stage 2B
Now, cancer has spread to other pelvic organs.
Stage 2C
Here in this stage, the tumor can be categorized in either stage 2A or stage 2B and some of the conditions may also be present such as Ascites that contain malignant cells or with positive peritoneal washings, the capsule has broken, and the tumor is there on the outer surface of one or both ovaries.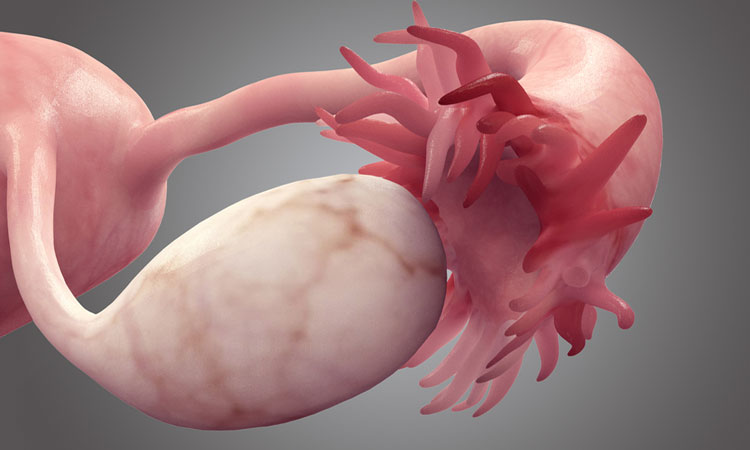
Stage 3
One or both ovaries may be involved by the cancer growth and some other conditions may also be there such as cancer may have spread to lymph nodes and cancer may also spread beyond the pelvis to the abdomen lining.
Stage 3A
cancer may involve one or both the ovaries.
Cancer can be seen in the abdomen but has not spread to lymph nodes.
Stage 3B
Presence of the tumor is there in one or both ovaries, and the cancer deposits can be seen in the abdomen.
These deposits are of about 2cm in diameter that makes them easy for a surgeon to view.
Lymph nodes are not affected by cancer.
Stage 3C
Presence of the tumor can be seen in one or both ovaries, and some of the conditions may also be there such as the cancer deposits that are not more than 2 cm in diameter and can be found in the abdomen, and cancer has spread to lymph nodes.
Stage 4
The Fourth stage is considered as the most advanced stage of ovarian cancer.
The growth of cancer includes one or both ovaries and distant metastases have also occurred.
In this advanced stage, the ovarian cancer cells can be found in pleural fluid.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
A pelvic exam is performed for examining the rectum, vagina, and lower abdomen for growths or masses.
If the growths are visible on ovaries, then certain other tests are also performed for producing detailed images of the ovaries.
Some of the tests include the followings:
- Exploratory Surgery: This surgery is performed for confirming the diagnosis of ovarian cancer.
- Ultrasound: High-frequency sound waves are produced to get precise images of the structures inside the body.
- Blood Tests: CA 125 blood test is performed for those women who are suspected of having ovarian cancer or previously had ovarian cancer.
This blood test helps in detecting a protein antigen that can be found at abnormally high levels in the blood serum of those women who have ovarian cancer. - Positron Emission Tomographic Scan (PET): This test helps in defining those areas that altered blood supply and helps in identifying cancer.
- Upper G.I. and Lower G.I. Scope: It helps in ruling out the primary cancer present in the G.I. tract.
- CT scan: This helps in generating two-dimensional images of the body that may show whether cancer has spread.
- Mammography: Metastatic tumors can be ruled out with this test.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Magnetic energy is used for generating highly detailed images of the anatomy such as tumors.
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
Radiation therapy, surgery, and chemotherapy are the treatment options for treating ovarian cancer.
Radiation Therapy
This therapy makes use of high-energy beams for destroying cancer cells.
This therapy helps in eliminating cancer that may be encompassed inside a radiation field.
This therapy can be either internally or externally delivered.
Internal radiation (Brachytherapy) is delivered by implanting a small amount of radioactive material surrounding cancer.
High-energy rays are delivered in external radiation that is directed to the tumor site through a machine outside the body.
Surgery
Three types of surgeries are involved in treating ovarian cancer such as the followings:
- Laparoscopy: The use of this minimally invasive surgery depends on the extent of cancer.
- Frozen Section Tissue Analysis: The rapid analysis of the tissue is done under a microscope.
The nature of the tumor is determined as to whether it is cancerous or non-cancerous that also helps surgeons to perform a suitable procedure during the first surgery. - Laparotomy: This procedure is used by making a large abdominal incision.
This incision is done for removing the uterus, ovaries, Fallopian tubes surrounding lymph glands, momentum (a fold of fatty tissue) and tumor.
Cytoreductive or debulking surgery is another name for this surgery.
Chemotherapy
Anticancer drugs are used for destroying the remaining cancer cells after surgery.
Women who have advanced ovarian cancer may be given chemotherapy as the initial treatment.
The injection of these drugs can be done in a vein or directly into the abdominal cavity.
These drugs can be either used alone or in combination.
Non-surgical Treatments
Biological Therapy
The activity of the cancer cells is changed with the help of biological therapy.
A type of biological therapy is known as Cetuximab that is also referred to as a monoclonal antibody.
The surface of the cancer cells that trigger the development of cancer cells is blocked with the help of Cetuximab.
Chemotherapy
This therapy makes use of drugs for destroying the cancer cells. The injection of these drugs is done into a vein.
Chemotherapy can also be combined with radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy destroys the cancer cell that may have traveled somewhere else in the body while radiotherapy destroys the cancer area.
Radiotherapy
This therapy makes use of radiation for destroying cancer cells.
This therapy shrinks the tumor by targeting a beam of radiation onto the cancer cells.
Rarely, a radioactivity source can be implanted in the mouth that is known as Brachytherapy.
This therapy does not damage the nearby tissues.