Cervical Cancer Treatment in Iran Details
What is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer begins with a narrow opening in the uterus from the vagina known as the cervix.
This cancer is considered as the most common cancer that develops in the cervix of a woman.
Cervical cancer usually occurs during the midlife.
Most women who are diagnosed with this cancer are in between 35-55 years of age.
This cancer has mostly diagnosed in around 20% of women who are older than 65.
Women who are under 20 rarely have this cancer.
Types of Cervical Cancer
The type of cervical cancer is determined by the type of cell where the early genetic mutation occurred.
The type also helps in determining the specific treatment for a patient.
There are two main types of cervical cancer that include the followings:
- Adenocarcinomas: This type takes place in the glandular cells lining the cervical canal.
Adenocarcinomas account for a smaller portion of all cervical cancers. - Squamous Cell Carcinomas: This type starts in the flat and thin cells lining the bottom of the cervix.
Squamous cell carcinomas make up for a vast majority of cervical cancers.
Small cell carcinomas, adenosquamous carcinomas, and clear cell carcinomas are considered as the less common types of cervical cancer.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is considered the most common cause of cervical cancer.
This virus can easily transmit to another person by having sexual contact with an HPV person.
The HPV virus has several types but not every type of HPV can cause cervical cancer.
Genital warts may be caused by them, and these different types also do not result in any symptoms.
The immune system of the body helps in fighting many infections.
Some diseases and medications can diminish the immune system that increases the chance of HPV infections, thus also increasing the chances of developing cervical cancer.
Smoking is yet another because that increases the chance of cervical cancer.
Environmental tobacco smoke and tobacco smoking relate to the development of cervical cancer.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer may not show any symptoms initially.
Other health conditions can also cause some essential symptoms of cervical cancer.
Some of the symptoms include the followings:
- Excess vaginal discharge
- Spotting in between periods or unusual vaginal bleeding
- Foul-smelling, watery or clear vaginal discharge
- Bleeding after intercourse or pain during sexual intercourse
When tumors invade other body organs, then it may result in some late symptoms that include the followings:
- Constipation
- Back or pelvic pain
- Blood in the stool
- Weight loss
- Anemia
- Urine leakage
- Shortness of breath
- Anorexia or appetite loss
Stages of Cervical Cancer
Stage 0: Here in this stage, cervix possesses no cancerous cells.
Some biological changes may cause the onset of cancer in the future, known as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN).
Stage 1: In the first stage, the cervix still holds cancer inside.
Stage 2: Now, in this stage, the spread of cancer is there outside the cervix in surrounding tissue or into the upper section of the vagina.
Stage 3: The spread of the cancer is there into the tissue of the pelvis or the lower section of the vagina.
Stage 4: At this last stage, cancer has spread to bladder or bowel and in its advanced case to the lungs.
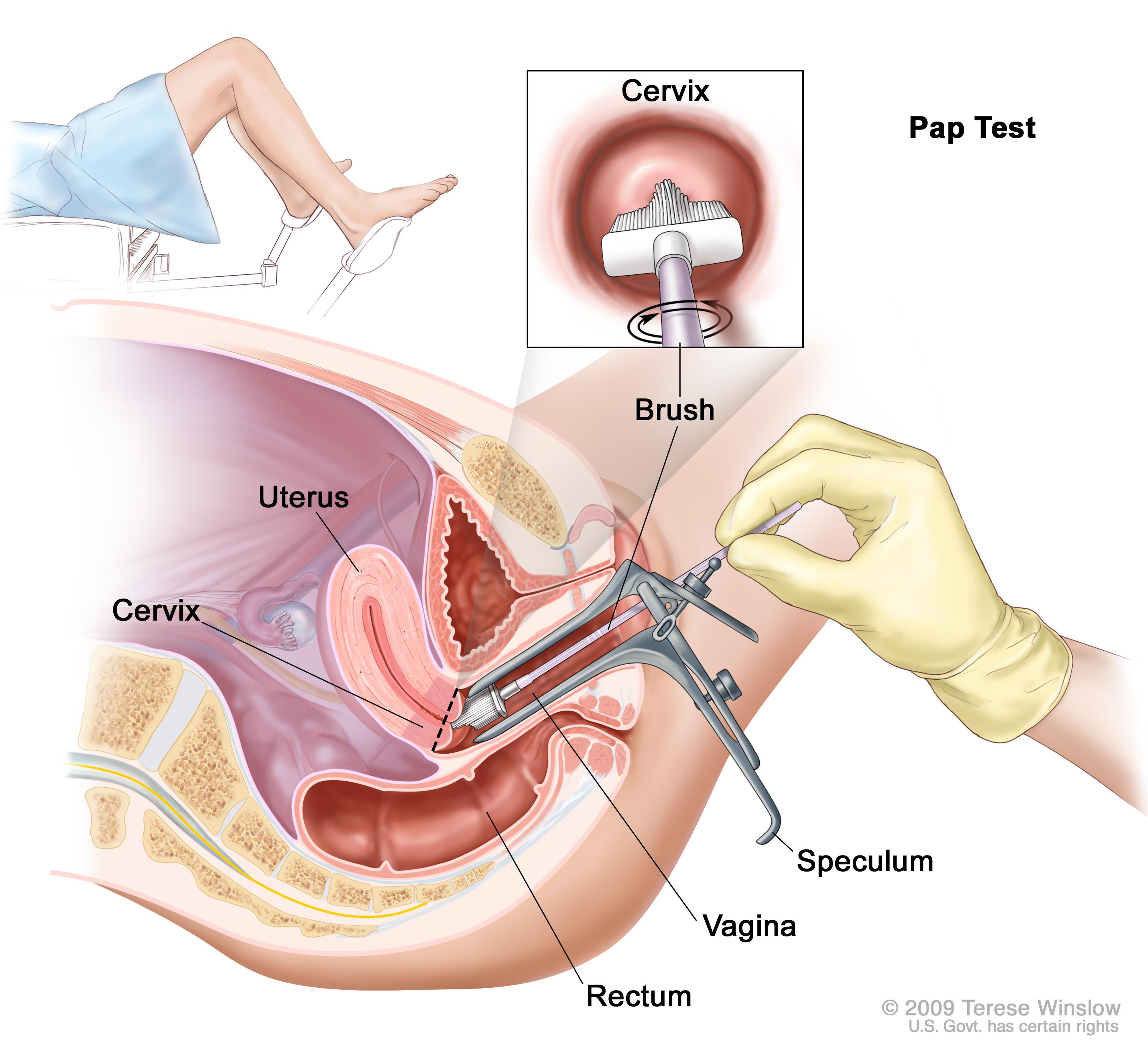
Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
A naked eye cannot see any precancerous changes of the cervix and cervical cancer.
Such conditions can be spotted by using tools and special tests.
- Cone Biopsy procedure can be performed.
- Pap smears are also performed for precancerous and cancer.
- The cervix is examined under magnification for observing abnormal changes, and this procedure is known as colposcopy.
This procedure surgically removes the tissue pieces, which are then examined in a laboratory.
Some other tests are also ordered when cervical cancer is diagnosed.
The spread of cancer can be easily determined with the help of these tests.
The different tests include the followings:
- MRI of the pelvis
- Chest x-ray
- Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
- CT scan of the pelvis
- MRI of the pelvis
- Cystoscopy
Treatment of Cervical Cancer
Health problems and the stage of cancer help in determining a specific treatment for cervical cancer.
Some of the treatment options include the followings:
- Radiation Therapy: High-powered energy is used in this therapy for destroying cancer cells.
Radiation therapy, when given internally, is performed by placing devices filled with radioactive material around the cervix.
External beam radiation is given when radiation therapy is performed externally.
These methods can also be combined. Chemotherapy is also sometimes combined with radiation therapy for destroying or shrinking a tumor that is remaining after surgery.
Menstruating may stop in premenopausal women due to radiation therapy and may start menopause. - Surgery: Early stages of cervical cancer are treated by surgically removing the uterus (hysterectomy).
The uterus, cancer, and cervix are removed by performing a hysterectomy.
This is a typical option when the cancer is at its early stage, and the invasion is less than 3mm inside the cervix. - Chemotherapy: Anti-cancer drugs are used in chemotherapy for killing cancer cells.
These drugs can be combined or can also be used alone.
The injection of these drugs is done into a vein that travels in the entire body and destroys all cancer cells.
Radiation therapy is often combined with low doses of chemotherapy as chemotherapy helps in enhancing the effects of the radiation.
Advanced cervical cancer that cannot be cured is treated by providing high doses of chemotherapy.