Lymphoma Cancer Treatment in Iran Details
What is Lymphoma Cancer?
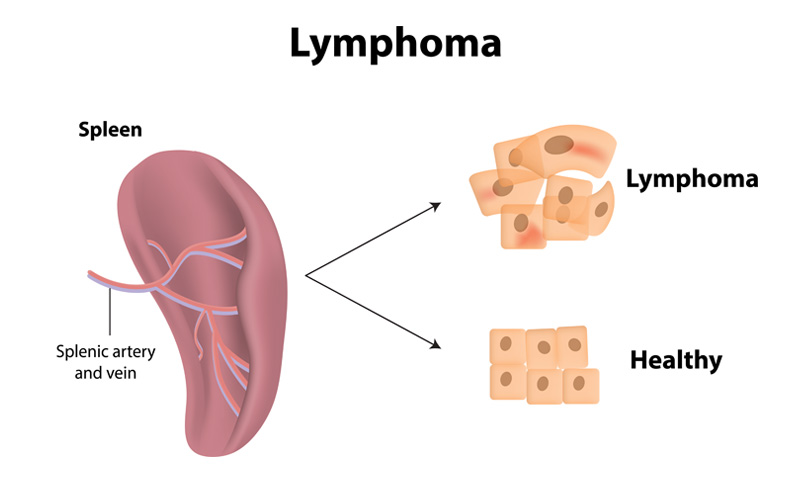
Cancer that starts in the immune system cells (lymphocytes) is known as lymphoma cancer.
The reason for lymphoma cancer is the uncontrollable growth of cells and their multiplication.
Lymphoma cancer can be categorized into two types, including the followings:
- Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)
Both Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma have many types.
Lymphoma can be categorized in a total of 30 different types in which some types are common while some are rare.
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, also known as Hodgkin’s disease, is one of the two common forms of lymphatic system cancers.
In Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, the cells present in the lymphatic system may grow unusually spreading beyond the lymphatic system.
A body may also lose its ability to fight against different infections due to the progression of Hodgkin’s disease.
There are no known causes of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
A slight risk of genetic predisposition and exposure to viral infections can be regarded as the causes of Hodgkin lymphoma.
Symptoms of Hodgkin Lymphoma
Swelling in the groin, neck, or armpit is considered as the most common symptom of Hodgkin lymphoma.
Some of the other symptoms include the followings:
- A persistent itch in the entire body
- Frequent sweat especially at night
- Breathlessness or cough
- Weight loss
- Unexplained high temperatures
- Tiredness
Some people are diagnosed with abnormal cells in their marrow that can result in a lower number of healthy blood cells in the blood.
Some of the symptoms due to the lower number of healthy blood cells include the followings:
- Excessive bleeding that includes hefty periods in women, nose bleeds and small blood spots under the skin
- Tiredness and breathlessness
- A higher risk of infection
Types of Hodgkin Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma can be categorized into different types that include the followings:
Nodular Lymphocyte – Predominant Type
This type is considered as rare, and approximately 5% of all Hodgkin lymphomas diagnosed are of a nodular lymphocyte-predominant type.
Classical Types
The four common types of Hodgkin lymphoma include the followings:
- Lymphocyte-rich
- Nodular sclerosing
- Lymphocyte-depleted
- Mixed cellularity
Hodgkin Lymphoma Stages
Stage 1
Here in this initial stage, the lymphoma affects only 1 group of lymph nodes.
Stage 2
In the second stage, two or more groups of lymph nodes are affected that are on the similar side of the diaphragm.
Stage 3
In the third stage, lymph nodes are affected below and above the diaphragm.
Stage 4
In the last stage, the spread of the lymphoma to the organs that are outside the lymph nodes include lungs, liver, or bones.
Diagnosis of Hodgkin Lymphoma
Swollen lymph nodes are one of the symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma that is associated with the diagnosis of lymphoma.
A biopsy is also carried out that helps in revealing the presence of Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Some of the other tests that help in checking the spread of lymphoma include the followings:
- Lumbar puncture
- Chest X-ray
- Blood tests
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans
- Bone marrow sample
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
- Computerized tomography (CT) scans
Treatment of Hodgkin Lymphoma
The specific treatment for Hodgkin lymphoma largely depends on the stage, overall health, and type of disease.
The aim is to kill all the present cancer cells.
Some of the treatment options include the followings:
Stem Cell Transplant
In this treatment, diseased bone marrow is replaced with healthy stem cells to grow new bone marrow.
This treatment can be the only option if Hodgkin lymphoma occurs again despite being treated.
The removal of a patient’s blood stem cells is done that is then stored and frozen for later use.
A patient then receives high-dose of radiation and chemotherapy for destroying cancerous cells in the body.
The stem cells are then softened and injected into the body using veins, and they then help in building new healthy bone marrow.
Chemotherapy
This therapy makes use of chemicals for destroying lymphoma cells.
These drugs travel to the bloodstream and finally reach to all parts of the body.
Radiation therapy is often combined with chemotherapy for treating those people who are suffering from early-stage classical type of Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Radiation Therapy
High-energy beams that include x-rays are used in this therapy for destroying cancer cells.
Radiation therapy is usually used after chemotherapy for treating classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Radiation therapy is used alone for treating those people who are suffering from early-stage lymphocyte-predominant of Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, also referred to as NHL or non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a type of cancer that begins in lymphocytes (a part of the immune system of the body).
NHL can be categorized into 40 different types.
There are no known causes of Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
People who have weak immune systems that also include those people, who are suffering from HIV infection or had an organ transplant, can develop Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Types of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
T-cell or B-cell lymphomas are categorized under lymphomas that depends on whether these lymphomas have begun from T-cell lymphocytes or B-cell lymphocytes.
B-cell lymphomas are considered as the most common that include the followings:
- Follicular lymphoma
- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Some of the not so common types include the followings:
- Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
- Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated tissue
- Small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL)
- Mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma
- Mantle cell lymphoma
- Nodal marginal zone lymphoma
- Burkitt lymphoma
T-cell lymphoma types include the followings:
- Lymphoblastic lymphoma
- Peripheral T-cell lymphoma
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma
- Skin (cutaneous) lymphoma
Symptoms of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Concentration problem, seizures, headache or personality changes can occur if the brain is affected by the cancer
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Abdominal swelling or pain results in vomiting, loss of appetite, nausea, and constipation
- Fever and chills that come and go
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin, neck and underarms areas
- Shortness of breath or coughing can occur when cancer affects lymph nodes or thymus gland in the chest that puts pressure on other airways or the windpipe
- Itching
Stages of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Stage 1
In the initial stage, the lymphoma affects only 1 group of lymph nodes.
Stage 2
The lymphoma in the second stage is present in 2 or more groups of lymph nodes on the same side of the diaphragm.
Stage 3
The lymphoma in the third stage is there on both sides of the diaphragm.
Stage 4
The lymphoma in the last change has spread beyond the lymph nodes to organs like lungs, bone marrow, or liver.
Diagnosis of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
A tissue biopsy is done for diagnosing Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
When there is a painless and enlarged lymph node that does not have an infection, then a biopsy is required.
Other tests include the followings:
- Spinal tap that depends on the location, stage, and type of the Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Blood tests
- Chest x-ray
- PET scan
- MRI scans for epidural or spinal lymphoma
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Upper GI endoscopy
- Computed tomography (CT) scans of the pelvis, chest, neck, and abdomen
- Testicular ultrasound is done for evaluating the opposite testicle for a testicular lymphoma primary site
- Upper GI series and small bowel x-rays
- Head and neck examination
Treatment of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
The treatment of Non-Hodgkin lymphoma depends on its stage, symptoms, and the type.
The treatment aims to eliminate the lymphoma without causing any damage to the surrounding cells.
The common treatment options for Non-Hodgkin lymphoma include the followings:
- Monoclonal Antibodies: This treatment is used for destroying lymphoma cells.
Monoclonal antibodies can also be combined with chemotherapy drugs for delivering a high concentration of the drugs to the tumor cells. - Chemotherapy: Anti-cancer drugs are used for destroying lymphoma cells that are injected through the vein or can also be taken by mouth.
This treatment has proved very beneficial for lymphoma as anti-cancer drugs enter the bloodstream that also reaches to every part of the body. - Radioimmunotherapy: This treatment uses a monoclonal antibody that also combines a radioactive particle to it.
This helps in destroying the lymphoma cells, and simultaneously, it also destroys many more cells that are in the radiation path. - Radiation Therapy: High dose x-rays are used for treating cancer cells that are still there after surgery.
This therapy is usually used for treating Non-Hodgkin lymphoma cancer.
External radiation is a method by which radiation is given directly to cancer from a machine that is outside of the body.